The Significance Of Mental Illness
Most people are curious about why people actually suffer from mental illness. By taking a step back and examining the science of mental illness you will be able to unlock the mystery behind mental illness and how it manifests itself.
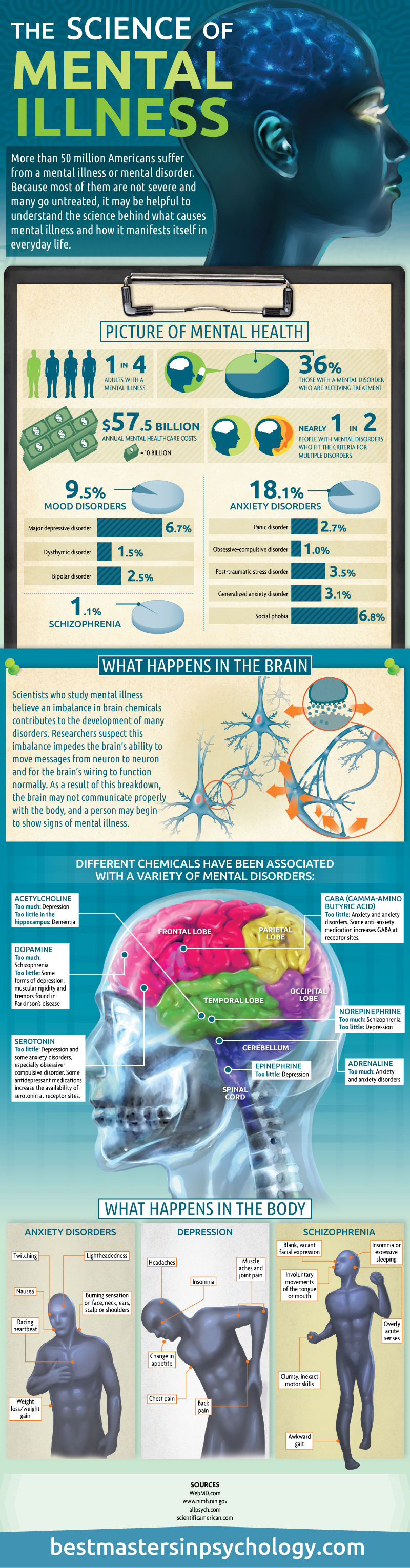
Statistics
Although mental illness affects 1 in every 4 adults, only 36% of people with a mental disorder actually receive treatment. Approximately 1 in every 2 people diagnosed as having a mental disorder may suffer from multiple disorders. Let’s take a look at the various types of mental disorders. Mood disorders, major depressive disorder, dysthymic disorder, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia account for 9.5%, 6.7%, 1.5%, 2.5%, and 1.1% of mental illness cases respectively. About 18.1% of people suffer from anxiety disorders. An accumulation of all mental disorder cases accounts $57.5 billion dollars on an annual basis.
Effects on the Brain
What actually happens in the brain of someone suffering from mental illness? Studies have shown that there is in fact a chemical imbalance which is responsible for the development of many mental disorders. Scientists believe that this chemical imbalance affects the brains ability to transmit messages from one neuron to another neuron therefore affecting the brains ability to function normally.
Chemical Effects on Mental Disorders
What chemicals are linked to mental disorders? Several different chemicals have been associated with mental disorders including acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, gaba (gamma-amino butyric acid, norepinephrine, adrenaline and epinephrine. Levels of these chemicals are not properly balanced in people with mental disorders. Too much acetylcholine causes depression and too little causes dementia. Excess amounts of dopamine causes schizophrenia and insufficient amounts causes depression, muscular rigidity and tremor like behaviors such as those present in people with Parkinson’s disease.
Too much serotonin is the major cause of depression and some anxiety disorders, primarily obsessive-compulsive disorder. Inadequate levels of gaba is linked to anxiety and anxiety disorders. An increased amount of norepinephrine is associated with schizophrenia while a scarce amount of norepinephrine is linked to depression. Too much adrenaline causes both anxiety and anxiety disorders while too little epinephrine is associated with depression.
Disorders and Mental Illness
Let’s examine what actually takes place in the body of someone who suffers from anxiety disorders, depression and schizophrenia. Anxiety disorders primarily affect your nerve impulses which causes twitching, lightheadedness, nausea, an accelerated heartbeat, as well as weight loss and weight gain. A burning sensation on the face, neck, ears, shoulders, or scalp is also common among people with anxiety disorders.
Depression
Depression is accompanied by headaches, insomnia, muscle aches, joint pain, changes in appetite, back pain, and chest pain. Schizophrenia causes a person to have blank, vacant facial expressions in addition to involuntary movement of the tongue and mouth. People with schizophrenia suffer from insomnia or excessive sleeping, inaccurate motor skills, extremely acute senses, and awkward gait.