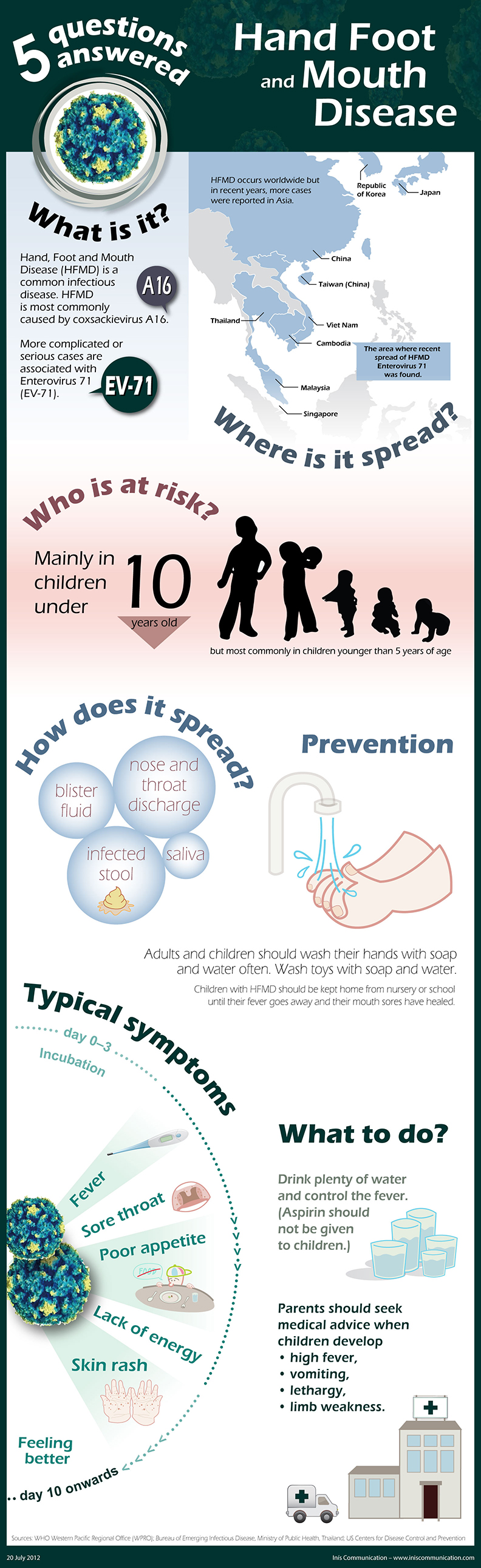
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD), despite the name, is actually a short, acute illness that affects mainly children. Children, however, do end up recovering from the condition in as much as a week.
About HFMD
This condition mainly originates from an infection, one that causes an illness that also causes symptoms like rash. The Coxsackie A16 virus is usually responsible for causing HFMD, though some cases are known to originate from enterovirus 71.
Most children under the age of 10 contract hand, foot and mouth disease. While this disease mainly affects children, older kids and adults do develop the disease. They usually develop a milder form of the illness, though some adults may develop severe symptoms. Most children don’t develop serious complications from having hand, foot and mouth disease.
The symptoms of HFMD are mainly characterized by an ‘unwell feeling’ that lasts about a day, the onset of fever and a sore throat. Children also end up developing small discolored spots in their mouth, which soon form into small mouth ulcers. Some cases depict children developing these spots on their skin.
Since it’s a viral condition, there’s no cure. Most treatment options for hand, foot and mouth disease revolve around making the patient as comfortable as possible while relieving the symptoms. The illness generally goes away after a week or so.
The Incubation Period of HFMD
The incubation period for HFMD is generally known to last as long as three to five days. Though, the incubation period for the illness is also known to last as short as two days and as long as two weeks. The incubation period generally marks the time that an infected child can potentially pass the condition to another uninfected person.
In most cases, the child can pass HFMD by coughing and/or sneezing, which can transmit the virus in the air. They can also pass the virus by touching others or surfaces if they haven’t washed their hands after touching face or mouth.
HFMD generally remains contagious until the spots and/or mouth ulcers disappear in children. Children, however, are known to remain relatively infectious for periods longer than two weeks.
During this time the virus may be passed through their stool long after their symptoms subside. To prevent them from potentially spreading the virus around, it’s important for parents to educate them about good hygiene practices.