Many people get confused particularly when it comes to having a clear understanding of how cellular division takes place. As tiny as it is, there are many processes that take place within a cell and contribute largely to the completion of an entire cycle. It is essential to mention that cell division consists of key processes such as mitosis and binary fission. All these processes have their own peculiar characteristics and, therefore, differ from each other in terms of how they take place. Many people tend to confuse binary fission and mitosis since both of them are a sexual form of reproduction.
Mitosis
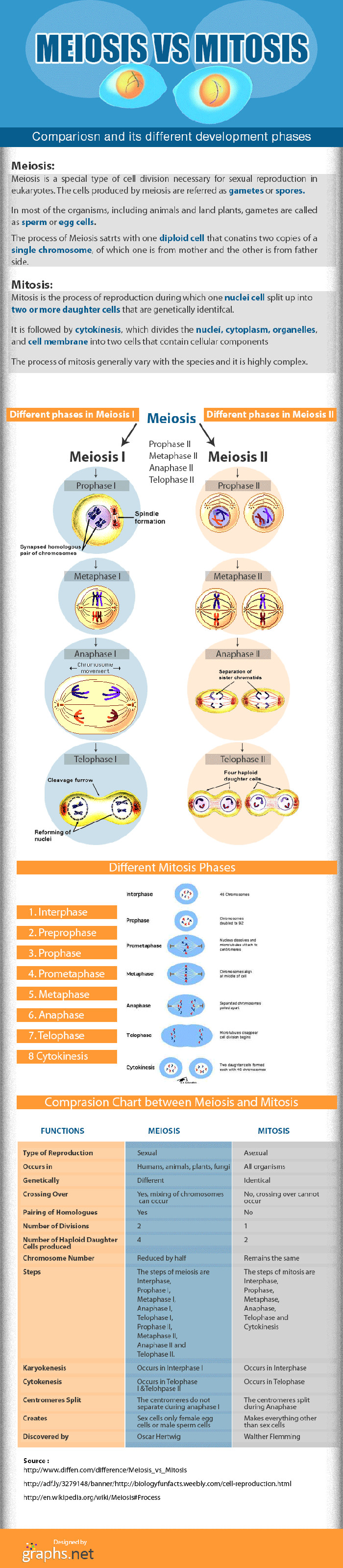
When a cell division takes place between somatic cells (non-sex cells), this process is referred to as mitosis. This is a replication process that leads to more cells during the formation and development of the embryo in animals and plants. The most distinct observation of the mitotic process is the production of two daughters that are identical with the same case applying to the original cell (in this case their mother).
There are four main stages that are associated with mitosis namely; G1, S, G2 and the last phase that ends the cycle. Inter-phase happens during the first three stages where cellular metabolic activity is at its peak. However, it’s important to mention that no chromosomal division takes place at this stage. A lot of activity is centered on the nucleus and cytoplasmic organs making this stage lengthy. RNA transcription is associated with G1 while DNA synthesis signifies the S phase. For the G2 phase, cells typically receive more energy and grow in size particularly the nucleolus.
Binary Fission
Binary fission is also referred to as prokaryotic fission and is known as the most popular and easy method of asexual reproduction. Unlike mitosis that has several stages in its cycle, binary fission, on the other hand, is brief and completes quickly. Here, there is no participation of the nuclear envelope and centromeres.
Binary fission is categorized into three types that are; simple, transverse and longitudinal. Simple binary fission takes place in amoebas. On the other hand, transverse binary fission occurs between paramecium and planaria in cases wherein cytoplasmic division plane resembles the specimen’s traverse axis. Longitudinal binary fission happens in the euglena when the plane resembles the longitudinal alignment.
Conclusion
The key difference between mitosis and binary fission is that the latter takes place among prokaryotes (cells with no nucleus) while mitosis takes place among eukaryotes (cells with a nucleus present).
Binary fission is a faster method of cellular division unlike mitosis whose process is lengthy and detailed.
Binary fission doesn’t have the elaborate four stages (G1 to final mitotic phase) that are witnessed in mitosis.