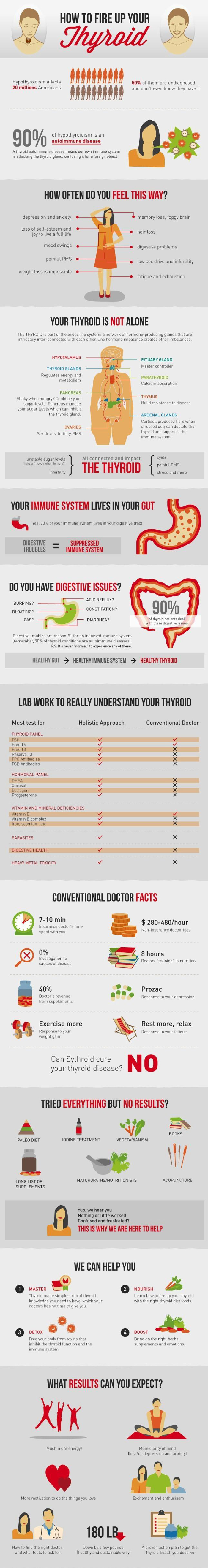
Hyperparathyroidism is an over activity of the body’s four parathyroid gland that results in excessive parathyroid hormones in the bloodstream. The parathyroid glands produce hormones are responsible for maintaining balance of calcium in the bloodstream and tissues, which depend on calcium to function properly.
The 15 Most Common Hyperparathyroid Symptoms
When hyperparathyroid symptoms occur, they result to damage or malfunction of other organs or tissues due to higher levels on calcium in the blood. Symptoms of the condition may vary from mild to severe. Symptoms of the condition include:
1. Fragile Bones (Osteoporosis and Osteopenia)
2. Excessive Urination
3. Abdominal Pain
4. Kidney Stones
5. Fatigue or Weakness
6. Forgetfulness and Depression
7. Nausea, loss of appetite, and vomiting
8. Bone and Joint Pain
9. Frequent Illness with no Particular Cause
10. Heartburn, gastric acid reflux, and GERD
11. High Blood Pressure
12. Thinning Hair
13. Heart Palpitations
14. Atrail Fibrillation
15. Lack of Sleep
It is recommended that you seek immediate medical help if you experience symptoms of hyperparathyroidism. These symptoms can be signs of underlying disorders, including serious complications. It is highly important to get accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for your condition.
Hyperparathyroidism Risk Factors
You may have high risk of developing hyperparathyroidism if you are a female who has gone through menopause, have had prolonged and severe deficiency in Vitamin D and calcium, and have had radiation treatment. People who have had taken lithium as medication for bipolar disorder and have rare, inherited disorder are also at high risk to hyperparathyroidism.
The Top 4 Complications Associated With Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism complications are similar to long term effects of high levels of calcium in the blood, and lower levels of calcium in the bones. Common complications that may result from the condition include:
1. Neonatal Hyperparathyroidism
Untreated hyperthyroidism to pregnant women can result to lower levels of calcium of their newborns.
2. Osteoporosis
Lower levels of calcium in the bones often results in weak and brittle bones that can get easily fracture and osteoporosis in aging people.
3. Cardiovascular Diseases
High levels of calcium in the bloodstream is associated to cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, and other types of heart diseases.
4. Kidney Stones
Excess amount of calcium in the bloodstream may lead to small, hard calcium deposits other substances to form in the kidneys.
Hyperparathyroidism Tests and Diagnosis
A series of blood tests is needed to treat a person with hyperparathyroidism. If the blood tests results indicate that the patient has high levels of calcium in the blood, the doctor will require fasting or not eating for a certain period of time. After you have fasted, the doctor will repeat the blood test to confirm the results. There are numbers of conditions that can raise the calcium levels in the blood, but the doctor can rule out the condition if the results of the blood tests indicate that the patient also has high levels of parathyroid hormone in the bloodstream. Other tests and diagnosis implemented to determine if the patient has hyperparathyroidism include urine tests, imaging tests of kidneys, ultrasound, sestamibi scan, and bone mineral density test.